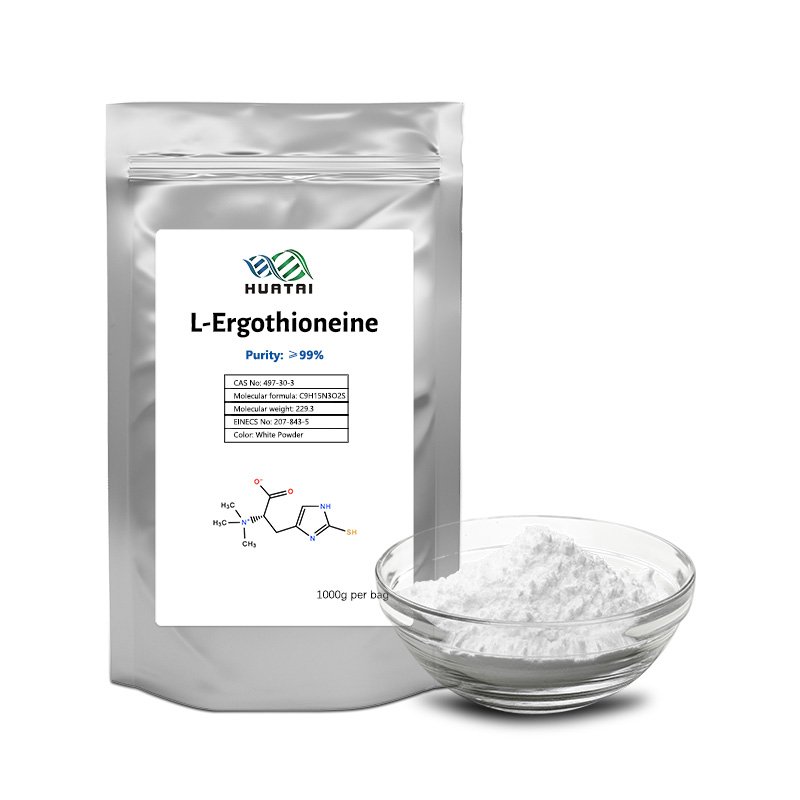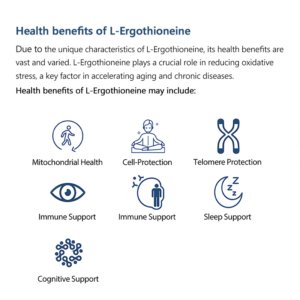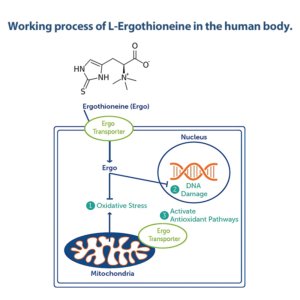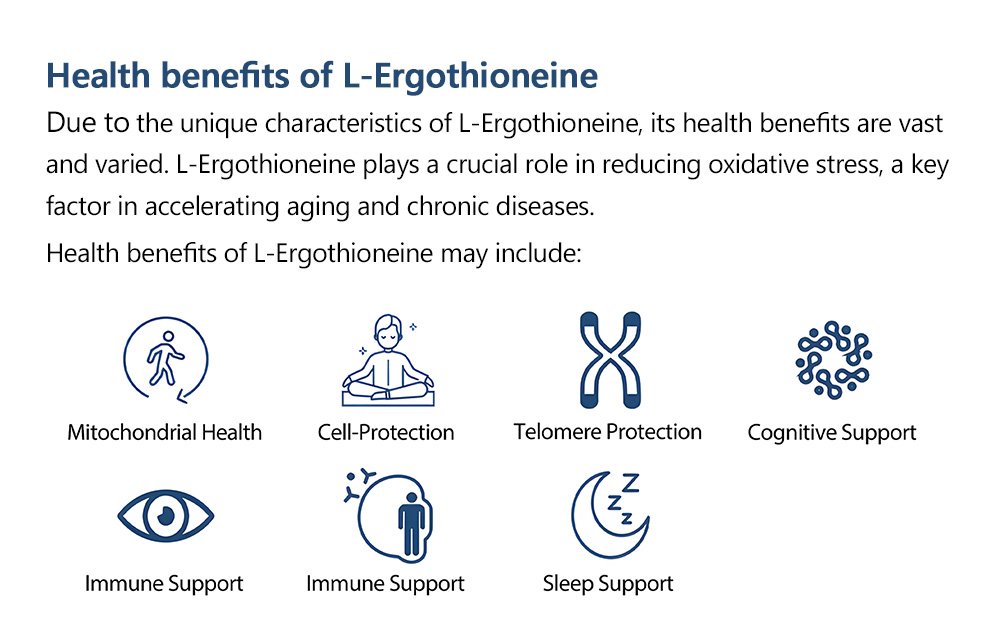
What is L-Ergothioneine?
L-Ergothioneine (EGT) is a sulfur-containing derivative of the amino acid histidine, first discovered in 1909 in ergot fungi. It naturally occurs in various foods, particularly in certain edible mushrooms such as shiitake, oyster, and maitake. Smaller amounts can also be found in black beans, red beans, organ meats, and whole grains. However, the human body cannot synthesize EGT—it must be obtained through the diet.
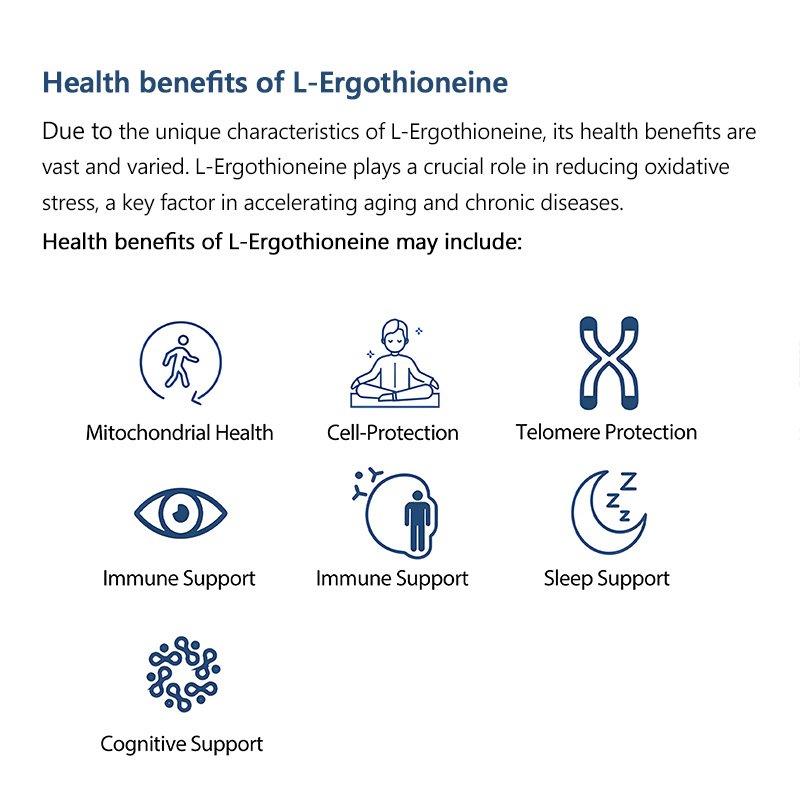
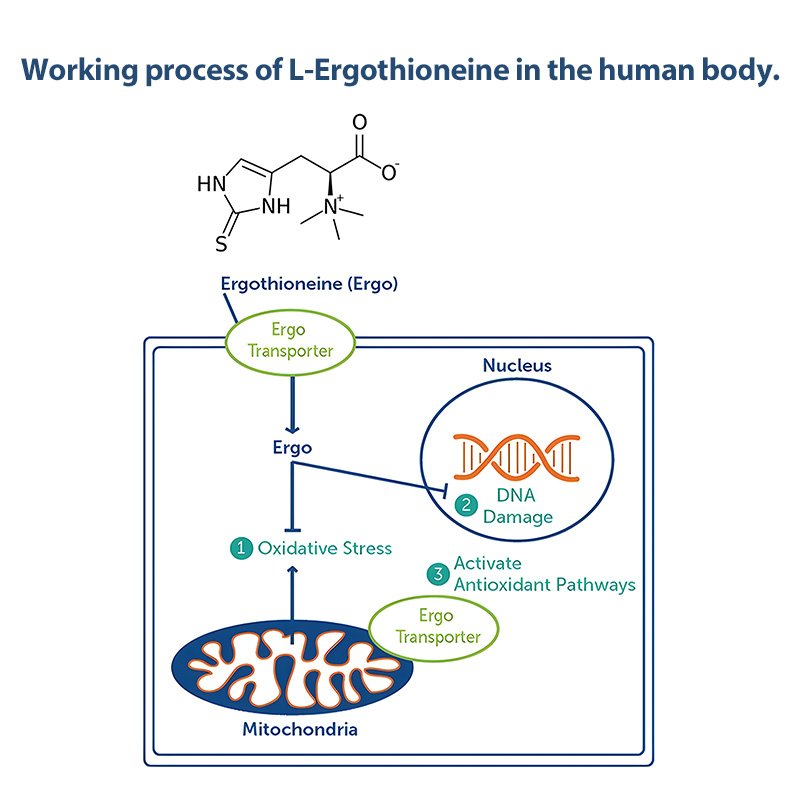
EGT is recognized for its potent antioxidant properties, which help neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative stress. Scientific studies have indicated its potential roles in cellular health, immune support, neuroprotection, cardiovascular health, and even anti-aging benefits
product efficacy
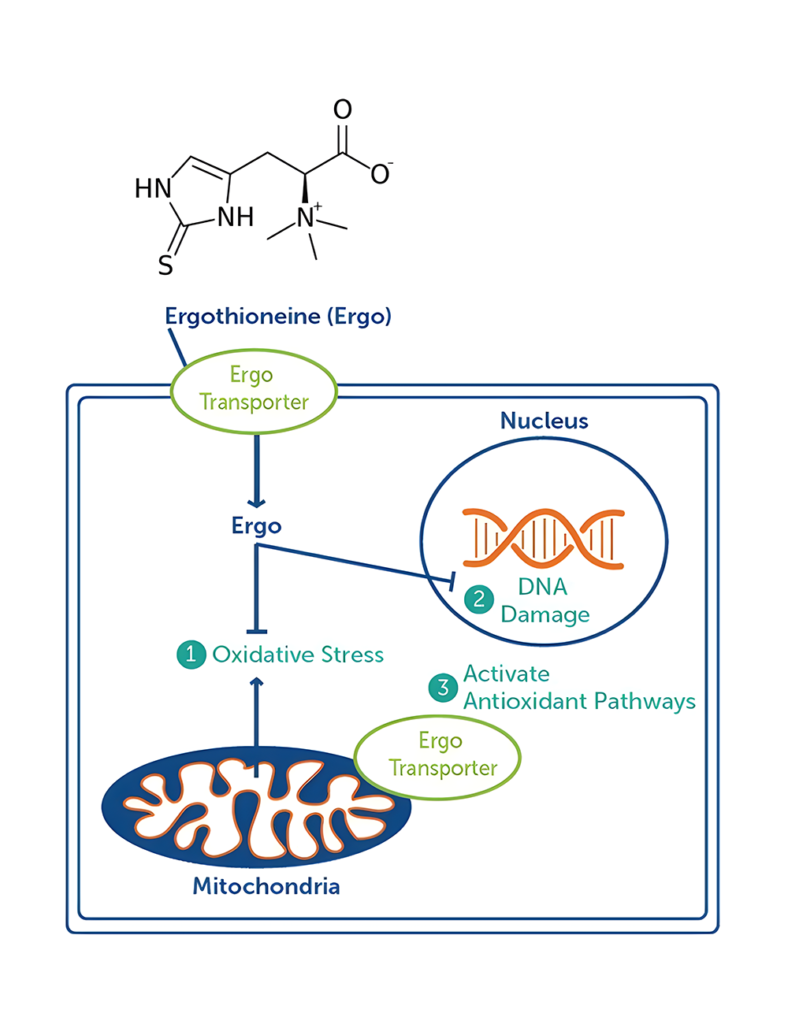
Antioxidant Mechanism of EGT
Glabridin has many effects and is praised as “Whitening Gold”. It can strongly resist bacteria, prevent inflammation, pigmentation and rough skin caused by ultraviolet rays. It can remove superoxide ions, inhibit hemolysis, highly inhibit the activity of tyrosinase and the activities of dopachrome tautomerase and DHICA oxidase. It is an excellent additive for whitening and freckle-removing cosmetics. It also has the ability to remove oxygen free radicals similar to SOD and vitamin E. At the same time, it has antioxidant and anti-atherosclerotic effects and also has certain effects of lowering blood lipid and blood pressure.
Research-Backed Benefits
Cardiovascular Support
Neuroprotection
Anti-Aging and Skin Health
Application Fields
Nutritional Supplements: EGT is incorporated into dietary supplements to support overall health and immune function.
Functional Foods and Beverages: Thanks to its stability, EGT can be added to beverages, cereal bars, dairy products, and chocolate to enhance antioxidant content (efsa.europa.eu).
Cosmetics: EGT is valued in cosmetics for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and moisturizing effects, contributing to healthier skin.
Safety and Regulatory Status
EGT’s safety has been validated by several health authorities. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted it GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status, allowing its use in foods, beverages, and dietary supplements . Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has assessed synthetic EGT and deemed it safe under proposed usage conditions .
Market Outlook
Scientific Research on L-Ergothioneine
1. Neuroprotection and Cognitive Health
A study published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia revealed that lower plasma levels of ergothioneine are associated with greater neurodegeneration and cerebrovascular damage in individuals with cognitive impairment and dementia. This suggests ergothioneine may help protect brain function.
🔗 Read the study
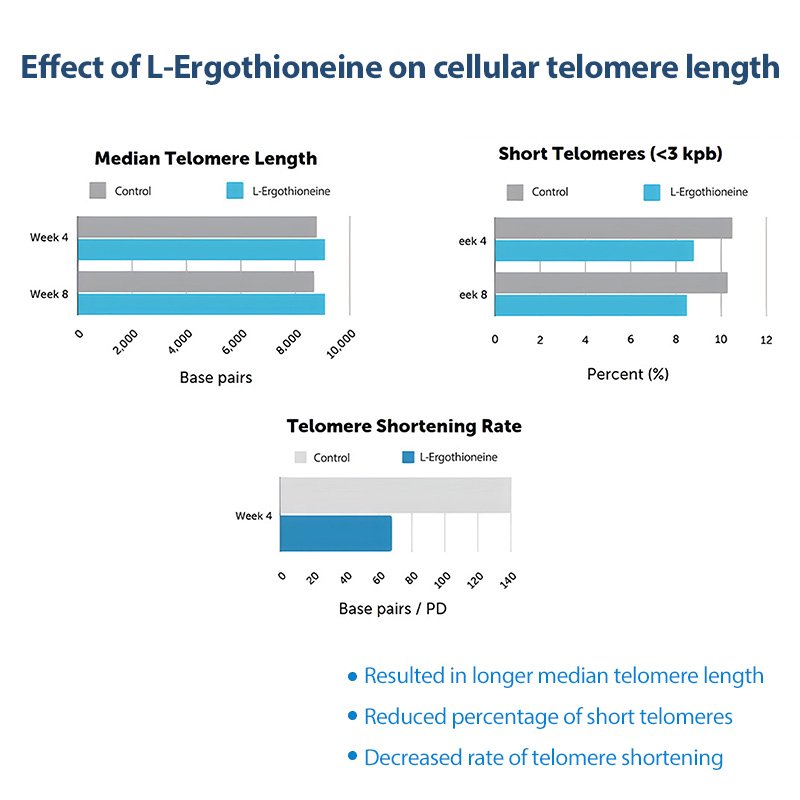
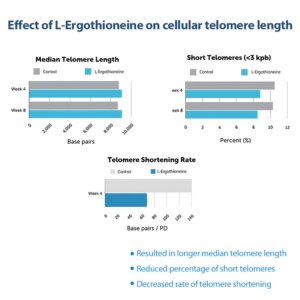
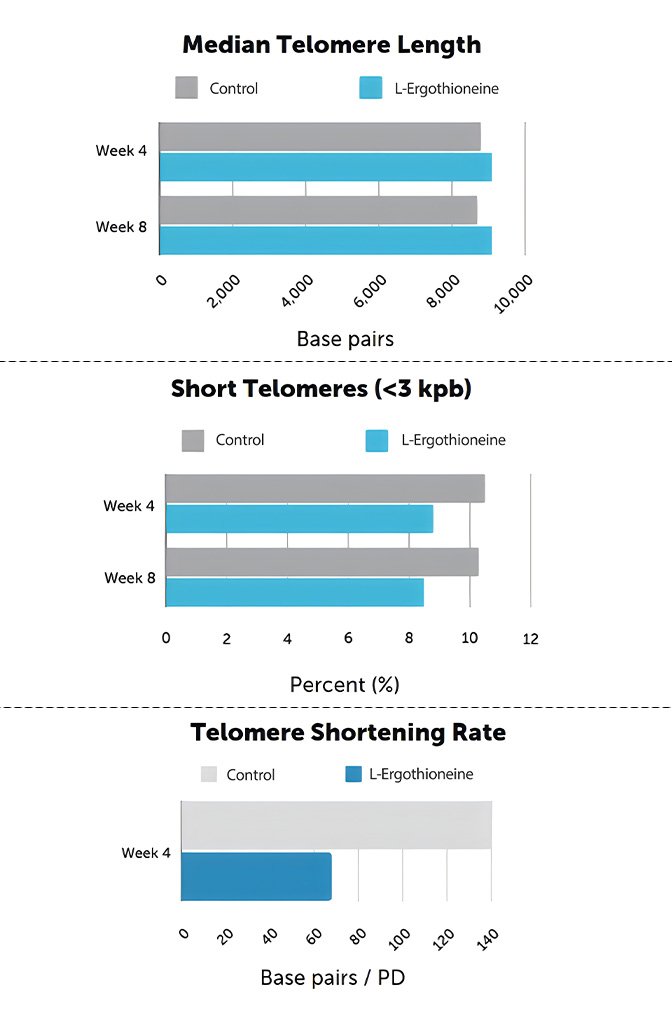
2. Anti-Aging and Telomere Preservation
A 2020 study in the Journal of Dietary Supplements found that ergothioneine helped protect telomeres—the protective caps of chromosomes—from oxidative damage, which may help slow cellular aging.
🔗 Read the study
3. Age-Related Hearing Loss
Research published in Hearing Research showed that L-Ergothioneine supplementation helped delay age-related hearing loss in male mice, suggesting a potential role in protecting against oxidative-stress-related auditory decline.
🔗 Read the study
4. Preeclampsia Support
A study published in Hypertension found that L-Ergothioneine significantly improved symptoms of preeclampsia in a preclinical model. This opens potential for EGT as a therapeutic approach for managing this serious pregnancy complication.
🔗 Read the study
5. Depression and Brain Regeneration
Research in FEBS Letters demonstrated that oral administration of ergothioneine in mice produced antidepressant-like effects and promoted the growth of new neurons in the hippocampus—pointing to its potential use in mental wellness.
🔗 Read the study